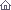
 This homemade metal detector circuit will help you find objects composed of materials with relatively high magnetic permeability. It is not suitable for buried coins discovery that is not sensitive enough but you can detect pirates treasures! This homemade metal detector circuit will help you find objects composed of materials with relatively high magnetic permeability. It is not suitable for buried coins discovery that is not sensitive enough but you can detect pirates treasures!
The metal detector is powered by 2 x 9V batteries, each of it charges with 15 mA. L1 detector coil is part of the sinusoidal oscillator built around transistor T1. Normally, the center frequency of the voltage controlled oscillator (VCO) from the PLL loop that is contained in IC1 is equal to the oscillation frequency of T1. This changes when entering a metallic object (ferrous or nonferrous) in the field induced by L1. S1 is a miniature 2-pole switch.
Meter needle deviation is a measure of frequency change, since the direction of deviation depends on the type of material detected by the coil.
The meter tool used for this homemade metal detector is zero as central, +-50µA.Coil L1 consists of 40 turns of enamelled copper wire, wound on a plastic template with a diameter of about 10 cm. Inductance thus obtained ensure the functioning of the oscillator at a frequency approximately equal to the VCO included in the PLL loop. Use an oscilloscope to check that pin 2 of IC1 delivers sinusoidal signal with frequency about 75 kHz. Adjust P1 so that fronts rectangular signal from pin 4 to coincide with the peaks of the sinusoidal signal from pin 2. Then, adjust P2 in order to obtain 0 on the meter. Since the neutral zero setting "runs” with the battery’s decreasing voltage it will be necessary to restore it (zero balancing) from time to time during use of the metal detector.
|